Physics

Feb 12th, 2026 - Follow Earth on Google A single trapped atom has been used to carry out Einstein's proposed test of the double-slit experiment, a challenge he believed could expose a flaw in quantum mechanics by measuring its recoil The laboratory result was decisive: any attempt to track a particle's path destroys the interference pattern, confirming Niels Bohr's claim that wave-like and particle-like behavior cannot be observed at the same time. Atoms, slits, and recoils Inside a modern experiment that ... [Read More]
Source: earth.com

Feb 11th, 2026 - Cheaper, brighter, and greener, perovskite LEDs could change lighting — if they last long enough. There's a new type of LED in town. These light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are made from a material called perovskite, a calcium titanium oxide mineral that is more closely associated with cheap solar panels. The perovskite LEDs are not only highly efficient and cheap to make but could also be more environmentally friendly than their predecessors. "Perovskite LEDs are cheaper and easier to ... [Read More]
Source: zmescience.com

Feb 4th, 2026 - Quantum physics paints a strange picture of the world, one filled with spooky connections, unsettling uncertainties and—perhaps oddest of all—particles that spontaneously spring into being from the void. These so-called virtual particles have indirect effects that scientists have measured before. But now, for the first time, researchers have traced the evolution of these something-out-of-nothing particles directly. In a study published today in Nature, physicists at the Relativistic ... [Read More]
Source: scientificamerican.com
Feb 4th, 2026 - An array of 15,000 qubits made from phosphorus and silicon offers an unprecedentedly large platform for simulating quantum materials such as perfect conductors of electricity An unprecedently large quantum simulator could shed light on how exotic, potentially useful quantum materials work and help us optimise them in the future. Quantum computers may eventually harness quantum phenomena to complete calculations that are intractable for the world's best conventional computers . Similarly, a ... [Read More]
Source: newscientist.com

Feb 2nd, 2026 - Why does time flow at all? Physicists struggle to find an answer The following essay is reprinted with permission from The Conversation , an online publication covering the latest research. Time feels like the most basic feature of reality. Seconds tick, days pass and everything from planetary motion to human memory seems to unfold along a single, irreversible direction. We are born and we die, in exactly that order. We plan our lives around time, measure it obsessively and experience it as an ... [Read More]
Source: scientificamerican.com
Physicists Reveal Hidden Geometry in Quantum Materials That Warps Electrons Like Gravity Bends Light

Feb 2nd, 2026 - This new discovery could pave the way for terahertz technology Imagine traveling through a city where the streets themselves change shape depending on how fast you drive down them. For tiny particles traveling close to the speed of light, such a thing may indeed be possible. Physicists have suspected that the microscopic world of electrons operates on a similarly shifting landscape, governed by a hidden geometry that warps their movement much like gravity bends the path of light around a ... [Read More]
Source: zmescience.com

Jan 25th, 2026 - Schrödinger's cat just got a little bit fatter. Physicists have created the largest ever 'superposition' — a quantum state in which an object exists in a haze of possible locations at once. A team based at the University of Vienna put individual clusters of around 7,000 atoms of sodium metal some 8 nanometres wide into a superposition of different locations, each spaced 133 nanometres apart. Rather than shoot through the experimental set up like a billiard ball, each chunky cluster ... [Read More]
Source: scientificamerican.com
Jan 11th, 2026 - Less than a trillionth of a second: Ultrafast UV light could transform communications and imaging. Scientists have developed a new platform that produces ultrashort UV-C laser pulses and detects them at room temperature using atom-thin materials. The light flashes last just femtoseconds and can be used to send encoded messages through open space. The system, from Light Publishing Center, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics And Physics, CAS, relies on efficient laser generation and ... [Read More]
Source: digitaljournal.com

Dec 28th, 2025 - As astrophysicists, we are trained to be cautious. New theories appear frequently, and most do not survive careful examination. Yet every so often, a framework emerges that does something unusual: it does not contradict what we already observe, it does not multiply speculative entities, and it does not demand that decades of experimental evidence be discarded. Instead, it quietly suggests that we may have misunderstood something fundamental. I recently encountered such a framework. It is known ... [Read More]
Source: ventsmagazine.com

Dec 25th, 2025 - Follow Earth on Google For centuries, most scientists have shared the belief that light behaves as both a wave and a particle. This idea, then, became the central component to quantum theory, sprouting the field of science known as quantum mechanics. The double-slit experiment supported the idea, showing bright and dark bands that indicated wave-like interference. But now, a new study suggests that this experiment might not lock us into seeing light as a wave. According to the experts, we can ... [Read More]
Source: earth.com

Nov 27th, 2025 - It's quick and easy to access Live Science Plus, simply enter your email below. We'll send you a confirmation and sign you up for our daily newsletter, keeping you up to date with the latest science news. In today's digital age, silicon is king. But as with other semiconductors that are widely used in the industry, trace quantities of other elements are often added to silicon to influence its electronic behaviour, a process known as doping. Now, scientists have taken doping to a new level, ... [Read More]
Source: livescience.com
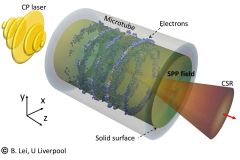
Nov 25th, 2025 - Researchers have designed a particle accelerator with nanotubes smaller than a human hair. We're used to seeing ever greater particle accelerators — colossal machines sprawling across landscapes, built to reveal the smallest details of the universe. Think of the Large Hadron Collider and its 27-kilometer-long ring, not to mention the $9 billion that went into its construction and operation thus far. But a new study from an international team of physicists, led by researchers at the ... [Read More]
Source: zmescience.com
CERN Scientists Trap a Record-Breaking 15,000 Antihydrogen Atoms and Supercharge Antimatter Research

Nov 24th, 2025 - CERN's ALPHA collaboration has pulled off a stunning breakthrough. Trapping antimatter is kind of like trying to catch snowflakes with a frying pan — if the snowflakes wanted to blow up the pan every time they touched it. That's basically the daily grind for CERN physicists who study antihydrogen. For years, they've been capturing these fragile anti-atoms one by one, inching toward answers about one of the universe's biggest mysteries. Now, they've made a major leap. The ALPHA ... [Read More]
Source: zmescience.com

Nov 24th, 2025 - Scientists link two distant quantum dots, teleporting information between their photons for the first time. Every message we send online, whether a bank transfer or a meme, relies on light. Tiny pulses travel through fiber-optic cables, bouncing between nodes that amplify the signal every few dozen kilometers. Your internet might come from your wireless carrier or WiFI, but broadband's backbone is still fiber-optic cables. But the quantum internet of the future — an ultra-secure network ... [Read More]
Source: zmescience.com

Nov 12th, 2025 - It's quick and easy to access Live Science Plus, simply enter your email below. We'll send you a confirmation and sign you up for our daily newsletter, keeping you up to date with the latest science news. Time crystals could help create quantum computing data storage that lasts minutes, new research shows — a huge improvement on the milliseconds-long duration of existing quantum data storage. In the new research, scientists ran experiments on how time crystals interact with mechanical ... [Read More]
Source: livescience.com
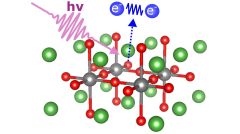
Nov 7th, 2025 - High-temperature superconductivity is still not fully understood. Now, an international research team at BESSY II has measured the energy of charge carrier pairs in undoped La₂CuO₄. Their findings revealed that the interaction energies within the potentially superconducting copper oxide layers are significantly lower than those in the insulating lanthanum oxide layers. These results contribute to a better understanding of high-temperature superconductivity and could also be relevant ... [Read More]
Source: phys.org