Space

Mar 12th, 2026 - Reading time 3 minutes Most gamma-ray bursts—the brightest, most powerful explosions in the universe—are tracked back to the deaths of massive stars . But a new discovery suggests that such enormous explosions can come from shockingly tiny galaxies—if the conditions align for particularly dense stars. In 2023, astronomers using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope spotted an unusual class of short gamma-ray bursts, whose origin appeared to be the ... [Read More]
Source: gizmodo.com

Mar 12th, 2026 - It's quick and easy to access Live Science Plus, simply enter your email below. We'll send you a confirmation and sign you up for our daily newsletter, keeping you up to date with the latest science news. Astronomers say a distant, sunlike star shows signs of a catastrophic planet-on-planet crash that may mirror the ancient impact that formed Earth's moon. Facebook X Whatsapp Reddit Pinterest Flipboard Join the conversation Add us as a preferred source on Google Get the Live Science Newsletter ... [Read More]
Source: livescience.com
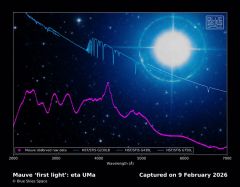
Mar 12th, 2026 - The world's first commercial space science telescope, Mauve, just sent back data from low-Earth orbit, achieving "first light" — and signaling a potential new era for low-cost observation. Launched Nov. 28, 2025, aboard SpaceX's Transporter-15 , Mauve was created by British space company Blue Skies Space to observe stars in ultraviolet light and help astronomers study how stellar flares affect whether exoplanets can support life. The small, suitcase-sized satellite and its 5-inch-aperture ... [Read More]
Source: astronomy.com

Mar 12th, 2026 - These confusing planets have shown that the trick to becoming huge lies in accretion. The universe rarely makes things easy to understand. For decades, researchers thought they had the recipe for a solar system figured out. You put a star in the middle, scatter some rocky crumbs nearby for things like Earth, and let the gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn sweep up the leftovers in the cold, dark suburbs. It was neat, tidy, and, as it turns out, probably wrong — or at least very incomplete. ... [Read More]
Source: zmescience.com

Mar 12th, 2026 - It's quick and easy to access Live Science Plus, simply enter your email below. We'll send you a confirmation and sign you up for our daily newsletter, keeping you up to date with the latest science news. Facebook X Whatsapp Reddit Pinterest Flipboard Join the conversation Add us as a preferred source on Google Get the Live Science Newsletter Get the world's most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox. By submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and ... [Read More]
Source: livescience.com

Mar 12th, 2026 - Reading time 3 minutes A recently discovered comet is plunging toward a fateful encounter with the Sun, which will determine whether it puts on a spectacular showing during the daylight or if it completely disintegrates into nothingness. Comet MAPS (C/2026 A1) is set for its perihelion, closest approach to the Sun, on April 4, when it will come within 99,000 miles (160,000 kilometers) from our host star, according to Space.com . That's incredibly close on a cosmic scale, and there's a ... [Read More]
Source: gizmodo.com

Mar 12th, 2026 - A groundbreaking study in galactic archaeology proves the Sun made a treacherous journey to reach its current home in the Milky Way suburbs. Our Sun is actually a cosmic refugee. Around 4.6 billion years ago, it first ignited in a hostile, radiation-blasted neighborhood 10,000 light-years closer to the Milky Way's center than it is now. Today, the Sun harbors a planetary system in the galactic suburbs. How did it cross that vast, treacherous distance? Now, an unprecedented study in galactic ... [Read More]
Source: zmescience.com

Mar 12th, 2026 - Although we may be loath to admit it, there sometimes appears to be a little magic in science. By magic, I refer to an overwhelming sense of wonder that accompanies surprising outcomes. Events over time — perhaps billions of years — can be folded together to produce a fascinating story. This is one of those stories. It begins in the early solar system, when violent impacts shaped a small world — and ends with those same forces leaving their mark on Earth, in ways that would ... [Read More]
Source: astronomy.com

Mar 11th, 2026 - Follow Earth on Google Astronomers have created the most detailed three-dimensional map yet of faint hydrogen light filling the universe roughly 9 to 11 billion years ago. Instead of showing galaxies as isolated points, the map reveals a vast web of diffuse glow stretching between them – light that has remained largely invisible in previous surveys. The discovery offers a new way to trace how matter gathered and how galaxies formed during one of the most active periods of cosmic history. ... [Read More]
Source: earth.com

Mar 11th, 2026 - A UC Berkeley theorist proposed that highly magnetized, spinning neutron stars were the power source behind superluminous supernovae. A recent supernova provided the smoking gun. , now a UC Berkeley theoretical astrophysicist and professor of physics, was the first to propose that a magnetar was powering the long-lasting glow. According to the theory, co-authored with Lars Bildsten and suggested independently by Stanford Woosley of UC Santa Cruz, when a massive star collapses at the end of its ... [Read More]
Source: news.berkeley.edu

Mar 11th, 2026 - Follow Earth on Google Mars took a direct hit from a powerful solar storm. The eruption from the Sun was one of the strongest recorded in more than two decades. The same storm struck Earth and triggered bright auroras that spread unusually far south, glowing in skies as far down as Mexico. Around Mars, spacecraft recorded something far more turbulent. Radiation levels spiked and the planet's upper atmosphere filled with charged particles. For a short time, the normally thin layers above the Red ... [Read More]
Source: earth.com

Mar 11th, 2026 - It's quick and easy to access Live Science Plus, simply enter your email below. We'll send you a confirmation and sign you up for our daily newsletter, keeping you up to date with the latest science news. Facebook X Whatsapp Reddit Pinterest Flipboard Join the conversation Add us as a preferred source on Google Get the Live Science Newsletter Get the world's most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox. By submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and ... [Read More]
Source: livescience.com

Mar 11th, 2026 - Follow Earth on Google Recent observations of our corner of the universe suggest we have been living inside a hot, less dense region, and that there may even be a strange "cosmic interstellar channel," or tunnel, connecting us to distant stars. After years of careful mapping, detailed analysis reveals what appears to be a channel of hot, low-density plasma stretching out from our solar system toward distant constellations. Astronomers from the Max Planck Institute recently confirmed it using ... [Read More]
Source: earth.com

Mar 10th, 2026 - The latest search for life on the headline – making exoplanet K2-18 b has come up empty. But the team says that they have developed a framework that could shape how scientists hunt for extraterrestrial life for years to come. In a study posted to the arXiv preprint server and accepted for publication by The Astrophysical Journal , researchers conducted one of the broadest and most sensitive technosignature searches ever in the K2-18 planetary system. Technosignatures are observable signs ... [Read More]
Source: astronomy.com

Mar 10th, 2026 - The lasers alone would cost around one trillion dollars and the technology to create a nanocraft does not yet exist. A new paper sketches a daring plan: launch a wafer-sized spacecraft toward the nearest black hole and let it report back on the most extreme physics in the cosmos. The author, astrophysicist Cosimo Bambi of Fudan University, places the idea "somewhere between hard engineering and science fiction," yet he also anchors it to a timeline. The hardware might be ready in twenty to ... [Read More]
Source: zmescience.com

Mar 10th, 2026 - Sixty-six light-years away, an Earth-sized exoplanet completes an orbit in under six hours, skimming around its star at nearly one-hundredth the distance that Mercury orbits the Sun. This planet is on the edge of destruction. Astronomer Fei Dai of the University of Hawai'i Institute for Astronomy and his team combined data from the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and Keck Planet Finder (KPF) to officially verify the world, called TOI-6255 b, as an exoplanet. The find enables ... [Read More]
Source: astronomy.com