Physics

Jan 5th, 2026 - An analysis of several experiments aimed at detecting the mysterious neutrino has identified a hint of a crack in the standard model of particle physics Notoriously ghostly particles called neutrinos may have revealed a crack in our understanding of all the particles and forces in the universe. The standard model of particle physics , which catalogues all the particles and forces we know to exist, is one of the biggest successes of modern physics, but physicists have also spent decades trying ... [Read More]
Source: newscientist.com

Dec 28th, 2025 - As astrophysicists, we are trained to be cautious. New theories appear frequently, and most do not survive careful examination. Yet every so often, a framework emerges that does something unusual: it does not contradict what we already observe, it does not multiply speculative entities, and it does not demand that decades of experimental evidence be discarded. Instead, it quietly suggests that we may have misunderstood something fundamental. I recently encountered such a framework. It is known ... [Read More]
Source: ventsmagazine.com

Dec 25th, 2025 - Follow Earth on Google For centuries, most scientists have shared the belief that light behaves as both a wave and a particle. This idea, then, became the central component to quantum theory, sprouting the field of science known as quantum mechanics. The double-slit experiment supported the idea, showing bright and dark bands that indicated wave-like interference. But now, a new study suggests that this experiment might not lock us into seeing light as a wave. According to the experts, we can ... [Read More]
Source: earth.com

Dec 7th, 2025 - The nature of time is one of the most profound and longstanding problems in physics – one that no one can agree on . From our perspective, time seems to steadily progress forward with each tick of the clock. But the closer we look, the more bizarre time becomes – from equations that state time should flow as freely backwards as it does forwards, to the strange quantum realm where cause and effect can flip on their heads. Could it even be that time itself is an illusion ? What makes ... [Read More]
Source: sciencefocus.com

Nov 27th, 2025 - It's quick and easy to access Live Science Plus, simply enter your email below. We'll send you a confirmation and sign you up for our daily newsletter, keeping you up to date with the latest science news. In today's digital age, silicon is king. But as with other semiconductors that are widely used in the industry, trace quantities of other elements are often added to silicon to influence its electronic behaviour, a process known as doping. Now, scientists have taken doping to a new level, ... [Read More]
Source: livescience.com
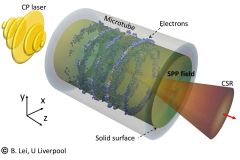
Nov 25th, 2025 - Researchers have designed a particle accelerator with nanotubes smaller than a human hair. We're used to seeing ever greater particle accelerators — colossal machines sprawling across landscapes, built to reveal the smallest details of the universe. Think of the Large Hadron Collider and its 27-kilometer-long ring, not to mention the $9 billion that went into its construction and operation thus far. But a new study from an international team of physicists, led by researchers at the ... [Read More]
Source: zmescience.com
CERN Scientists Trap a Record-Breaking 15,000 Antihydrogen Atoms and Supercharge Antimatter Research

Nov 24th, 2025 - CERN's ALPHA collaboration has pulled off a stunning breakthrough. Trapping antimatter is kind of like trying to catch snowflakes with a frying pan — if the snowflakes wanted to blow up the pan every time they touched it. That's basically the daily grind for CERN physicists who study antihydrogen. For years, they've been capturing these fragile anti-atoms one by one, inching toward answers about one of the universe's biggest mysteries. Now, they've made a major leap. The ALPHA ... [Read More]
Source: zmescience.com

Nov 24th, 2025 - Scientists link two distant quantum dots, teleporting information between their photons for the first time. Every message we send online, whether a bank transfer or a meme, relies on light. Tiny pulses travel through fiber-optic cables, bouncing between nodes that amplify the signal every few dozen kilometers. Your internet might come from your wireless carrier or WiFI, but broadband's backbone is still fiber-optic cables. But the quantum internet of the future — an ultra-secure network ... [Read More]
Source: zmescience.com
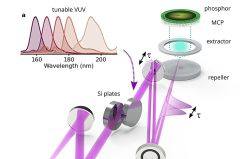
Nov 7th, 2025 - A team of researchers at the Max Born Institute have managed to fully characterize few-femtosecond-long light pulses tunable in the vacuum ultraviolet. These results unlock the possibility for studying valence electron dynamics of many materials in the VUV. The research is in the journal Nature Photonics . Few-femtosecond long pulses tunable across the ultraviolet (UV) are a holy grail of contemporary laser science. As most of the materials have electronic resonances in the deep- and vacuum-UV ... [Read More]
Source: phys.org
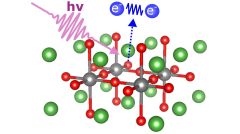
Nov 7th, 2025 - High-temperature superconductivity is still not fully understood. Now, an international research team at BESSY II has measured the energy of charge carrier pairs in undoped La₂CuO₄. Their findings revealed that the interaction energies within the potentially superconducting copper oxide layers are significantly lower than those in the insulating lanthanum oxide layers. These results contribute to a better understanding of high-temperature superconductivity and could also be relevant ... [Read More]
Source: phys.org

Nov 4th, 2025 - Follow Earth on Google A team led by MIT used a simple molecule to peek inside a radium atom's nucleus. In a new study, they watched electrons in radium monofluoride pick up a tiny energy change that betrays what is happening deep in the core. The tests ran on a compact setup at CERN in Switzerland and not in a collider that stretches for miles. The result points to a practical way to map nuclear structure and to probe why the universe favors matter over antimatter. Radium monofluoride reveals ... [Read More]
Source: earth.com
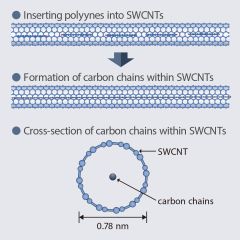
Oct 29th, 2025 - Carbynes, or long linear carbon chains (LLCCs), have received significant attention in recent years due to their predicted exceptional properties. However, experimentally, their properties have been hard to probe due to their low stability. To improve stability, it is necessary to encapsulate LLCCs in small diameter carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Now, researchers have developed a new method to synthesize small diameter single-walled carbon nanowires (SWCNWs), featuring high-density LLCCs encapsulated ... [Read More]
Source: phys.org
Oct 22nd, 2025 - The nature of gravity — and whether it can be reconciled with quantum mechanics — is one of the biggest mysteries in physics. Most researchers think that at a fundamental level, all phenomena follow the principles of quantum physics, but those principles do not seem to be compatible with the accepted theory of gravity. For years, researchers have been proposing experiments to show whether gravity could produce a phenomenon known as quantum entanglement. Now, two theoretical ... [Read More]
Source: nature.com

Oct 21st, 2025 - It's quick and easy to access Live Science Plus, simply enter your email below. We'll send you a confirmation and sign you up for our daily newsletter, keeping you up to date with the latest science news. GET LIVE SCIENCE PLUS Enter your email below to get the latest science news every day. We'll send you a confirmation and sign you up for our daily newsletter. By submitting your information, you confirm you are aged 16 or over, have read our and agree to the . Geographical rules apply. ... [Read More]
Source: livescience.com

Oct 20th, 2025 - In the right combinations and conditions, two-dimensional materials can host intriguing and potentially valuable quantum phases, like superconductivity and unique forms of magnetism. Why they occur, and how they can be controlled, is of considerable interest among physicists and engineers. Research published in reveals a previously hidden feature that could explain how and why enigmatic quantum phases emerge. Using a new terahertz (THz) spectroscopic technique, the researchers revealed that ... [Read More]
Source: phys.org
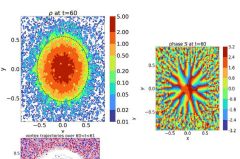
Oct 18th, 2025 - The nature of dark matter remains one of the greatest mysteries in cosmology. Within the standard framework of non-collisional cold dark matter (CDM), various models are considered: WIMPs (Weakly Interacting Massive Particles, with masses of around 100 GeV/c 2 ), primordial black holes, and ultralight axion-like particles (mass of 10 -22 to 1 eV/c 2 ). In the latter case, dark matter behaves like a wave, described by a Schrödinger equation, rather than as a collection of point particles. ... [Read More]
Source: phys.org